Portal:Myanmar
Portal maintenance status: (March 2022)
|

Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar and also referred to as Burma (the official English name until 1989), is a country in northwest Southeast Asia. It is the largest country by area in Mainland Southeast Asia and has a population of about 55 million. It is bordered by India and Bangladesh to its northwest, China to its northeast, Laos and Thailand to its east and southeast, and the Andaman Sea and the Bay of Bengal to its south and southwest. The country's capital city is Naypyidaw, and its largest city is Yangon (formerly Rangoon).
Myanmar is a member of the East Asia Summit, Non-Aligned Movement, ASEAN, and BIMSTEC, but it is not a member of the Commonwealth of Nations despite once being part of the British Empire. Myanmar is a Dialogue Partner of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization. The country is very rich in natural resources, such as jade, gems, oil, natural gas, teak and other minerals, as well as endowed with renewable energy, having the highest solar power potential compared to other countries of the Great Mekong Subregion. However, Myanmar has long suffered from instability, factional violence, corruption, poor infrastructure, as well as a long history of colonial exploitation with little regard to human development. In 2013, its GDP (nominal) stood at US$56.7 billion and its GDP (PPP) at US$221.5 billion. The income gap in Myanmar is among the widest in the world, as a large proportion of the economy is controlled by cronies of the military junta. Myanmar is one of the least developed countries. Since 2021, more than 600,000 people have been displaced across Myanmar due to the civil war post-coup, with more than three million people in dire need of humanitarian assistance. According to the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR), there are over 1.3 million people counted as refugees and asylum seekers, and 3.5 million people displaced internally as of December 2024. (Full article...)
Selected articles - load new batch
-
Image 1The 1962 Burmese coup d'état marked the beginning of one-party rule in Burma (Myanmar) and the political dominance of the military in Burmese politics. In the 2 March 1962 coup, the military replaced the civilian AFPFL-government headed by Prime Minister U Nu with the Union Revolutionary Council Chaired by General Ne Win.
In the first 12 years following the coup, the country was ruled under martial law, and saw a significant expansion in the military's role in the national economy, politics, and state bureaucracy. Following the constitution of 1974, the Revolutionary Council handed over the power to the elected government, consisting of a single-party, the Burma Socialist Programme Party, which had been founded by the council in 1962. The elected government remained hybrid between civilian and military, until 18 September 1988, when the military again took over as the State Law and Order Restoration Council (then renamed the State Peace and Development Council) following the nationwide 8888 Uprising and virtual breakdown of the socialist regime. The military junta retained power for 23 years until 2011, when it was transferred to the Union Solidarity and Development Party. (Full article...) -
Image 2Cadets of the Kachin Independence Army (KIA) preparing for military drills at the group's headquarters in Laiza, Kachin State.
The Kachin conflict or the Kachin War is one of the multiple conflicts which are collectively referred to as the internal conflict in Myanmar. Kachin insurgents have been fighting against the Tatmadaw (Myanmar Armed Forces) since 1961, with only one major ceasefire being brokered between them, which lasted from 1994 to 2011, a total of 17 years.
Since the resumption of hostilities in 2011, thousands of civilians have been killed, whilst over 100,000 more have been displaced. Widespread use of landmines, child soldiers, systematic rape and torture have been alleged by both sides. (Full article...) -
Image 3

Burma was under the military dictatorship of Ne Win from 1962 to 1988. Ne Win and his allies in the Tatmadaw – the country's armed forces – overthrew the government of Prime Minister U Nu in a coup d'état on 2 March 1962. A day later, the coup leaders established the Revolutionary Council of the Union of Burma as the country's governing body. In April 1962, the Revolutionary Council introduced the Burmese Way to Socialism and declared it Burma's state ideology. The Revolutionary Council then founded the Burma Socialist Programme Party (BSPP) as the country's vanguard party on 4 July 1962. In 1974, Ne Win introduced a new constitution and replaced the Revolutionary Council with the People's Assembly, which consisted solely of BSPP members. The country's official name was also changed from the Union of Burma to the Socialist Republic of the Union of Burma.
Ne Win's governance of Burma was characterised by totalitarianism, isolationism, superstition, xenophobia, and a rejection of Cold War politics. Ne Win ruled Burma as a dictator, serving as both Chairman of the Revolutionary Council (later President of Burma) and Prime Minister of Burma, the country's head of state and the head of government, respectively. The nationalisation of major industries and rejection of foreign investment led to catastrophic declines in economic growth and living standards. (Full article...) -
Image 4
Lake of No Return, also referred to as Naung Yang in Tai languages, is a body of water in Myanmar, lying in the area of the Pangsau Pass (3727') on the India–Myanmar border south of Pangsau (also called Pansaung) village. The lake is 1.4 km in length and 0.8 km in width at its widest part. It is located 2.5 km to the southwest of the Ledo Road, formerly called Stilwell Road, the road the Western Allies started building in 1942 to supply the Chinese armies of Chiang Kai-shek.
The area is home to the Tangsa community. Since the improvement of relations between India and Myanmar , the lake has come to play a part in the development of tourism in the nearby Indian Changlang District, which borders Myanmar. (Full article...) -
Image 5The Myanmar civil war (Burmese: မြန်မာ့ပြည်တွင်းစစ်), also known as the Burmese civil war, is an ongoing civil war since 2021. It began following Myanmar's long-running insurgencies, which escalated significantly in response to the 2021 coup d'état and the subsequent violent crackdown on anti-coup protests. The exiled National Unity Government (NUG) and major ethnic armed organisations repudiated the 2008 Constitution and called instead for a democratic federal state. Besides engaging this alliance, the ruling government of the State Administration Council (SAC), also contends with other anti-SAC forces in areas under its control. The insurgents are apportioned into hundreds of armed groups scattered across the country.
As of March 2023 the United Nations estimated that since the coup in February 2021, 17.6 million people in Myanmar required humanitarian assistance, while 1.6 million were internally displaced, and over 55,000 civilian buildings had been destroyed. The United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (UNOCHA) said that over 40,000 people had fled into neighboring countries, such as Bangladesh, India and Thailand. (Full article...) -
Image 65.5-inch guns of the Royal Artillery firing on Japanese troops attempting to break out of the Sittang Bend in early August 1945
The Battle of the Sittang Bend and the Japanese Breakout across Pegu Yomas were linked Japanese military operations during the Burma Campaign, which took place nearly at the end of World War II. Surviving elements of the Imperial Japanese Army who had been driven into the Pegu Yoma attempted to break out eastwards in order to join other Japanese troops retreating from the British forces. The break-out was the objective of the Japanese Twenty-Eighth Army with support at first from the Thirty-Third Army and later the Fifteenth Army. As a preliminary, the Japanese Thirty-Third Army attacked Allied positions in the Sittang Bend, near the mouth of the river, to distract the Allies. The British had been alerted to the break-out attempt and it ended calamitously for the Japanese, who suffered many losses, with some formations being wiped out.
There were around 14,000 Japanese casualties, with well over half being killed, while British forces suffered only 95 killed and 322 wounded. The break-out attempt and the ensuing battle became the last significant land battle of the Western powers in the Second World War. (Full article...) -
Image 7The University of Yangon (also Yangon University; Burmese: ရန်ကုန် တက္ကသိုလ်, pronounced [jàɰ̃ɡòʊɰ̃ tɛʔkəθò]; formerly Rangoon College, University of Rangoon and Rangoon Arts and Sciences University), located in Kamayut, Yangon, is the oldest university in Myanmar's modern education system and the best known university in Myanmar. The university offers mainly undergraduate and postgraduate degrees (Bachelor's, Master's, Post-graduate Diploma, and Doctorate) programs in liberal arts, sciences and law. Full-time bachelor's degrees were not offered at the university's main campus after the student protests of 1996. The bachelor's degree was re-offered from 2014 on. Today degrees in Political Science are offered to undergraduate students, as well as postgraduate diplomas in areas such as social work and geology.
Initially most major universities in the country depended on Yangon University. Until 1958 when Mandalay University became an independent university, all institutions of higher education in Myanmar were under Yangon University. After the University Education Act of 1964, all professional colleges and institutes of the university such as the Institute of Medicine 1, Rangoon Institute of Technology and Yangon Institute of Economics became independent universities, leaving the Yangon University with liberal arts, sciences and law. In Myanmar, responsibility for higher education depends on various ministries. The University of Yangon depends from the Ministry of education. (Full article...) -
Image 8
Nyi Nyi Lwin (Burmese: ညီညီလွင်; MLCTS: Nyi Nyi Lwang; born 19 June 1979), more widely known by his monastic name U Gambira (Burmese: ရှင်ဂမ္ဘီရ), is a former Buddhist monk, activist and a leader of the All-Burma Monks' Alliance, a group which helped lead the 2007 protests against Burma's military government. Following the protests, he went into hiding and published two editorials critical of the Burmese government in The Washington Post and The Guardian on 4 November 2007. He was arrested the same day.
In November 2008, he was sentenced to 68 years in prison, including 12 years hard labour; the sentence was reduced to 65 years on appeal. Gambira reportedly protested his imprisonment by organising chanting with other imprisoned monks, boycotting his trial, and going on hunger strike. Human rights groups including Amnesty International and Human Rights Watch also protested his imprisonment. (Full article...) -
Image 9Protesters in Yangon with a banner that reads "Non-violence: National Movement" in Burmese, in the background is Shwedagon Pagoda
The Saffron Revolution (Burmese: ရွှေဝါရောင်တော်လှန်ရေး, romanized: Shwaywarraung Tawlhaanrayy; [sw̥èi wà jàʊɰ̃ tɔ̀ l̥àɰ̃ jéi]) was a series of economic and political protests and demonstrations that took place during August, September, and October 2007 in Myanmar. The protests were triggered by the decision of the national military government to remove subsidies on the sales prices of fuel. The national government is the only supplier of fuels and the removal of the price subsidy immediately caused diesel and petrol prices to increase by 66–100% and the price of compressed natural gas for buses to increase 500% in less than a week.
The various protests were led by students, political activists, including women, and Buddhist monks and took the form of a campaign of nonviolent resistance, sometimes also called civil resistance. (Full article...) -
Image 10
The Ava Kingdom (Burmese: အင်းဝပြည်, pronounced [ʔɪ́ɰ̃wa̰ kʰɪʔ]; INN-wa pyi) also known as Inwa Kingdom or Kingdom of Ava was the dominant kingdom that ruled upper Burma (Myanmar) from 1365 to 1555. Founded in 1365, the kingdom was the successor state to the petty kingdoms of Myinsaing, Pinya and Sagaing that had ruled central Burma since the collapse of the Pagan Kingdom in the late 13th century.
Like the small kingdoms that preceded it, Ava may have been led by Bamarised Shan kings who claimed descent from the kings of Pagan. Scholars debate that the Shan ethnicity of Avan kings comes from mistranslation, particularly from a record of the Avan kings' ancestors ruling a Shan village in central Burma prior to their rise or prominence. (Full article...)
Did you know (auto-generated) - load new batch

- ... that the Burmese Buddhist monk Sagyo Thu-Myat successfully lobbied for the recalibration of the Burmese calendar?
- ... that while defending Zaw Myint Maung following his arrest by the Myanmar junta, lawyer Ywet Nu Aung was herself arrested and charged?
- ... that Maung O, Prince of Salin, and his sister Nanmadaw Me Nu became de facto rulers of Burma when King Bagyidaw was suffering from depression?
- ... that Burma the elephant once escaped Auckland Zoo?
- ... that Myinsaing withstood a ten-week siege by the Mongols because its three brother leaders bribed the invaders to withdraw?
- ... that the DI MA-1 Mk. III rifle was made in Myanmar as a reverse-engineered copy of the Chinese QBZ-97?
- ... that Molly Burman resumed releasing music three years later after finding that "Happy Things" had accrued a million streams on Spotify?
- ... that former Burmese actress Honey Nway Oo turned rebel and took up arms against the military junta following the 2021 Myanmar coup d'état?
Related portals and projects
General images - load new batch
-
Image 1Hlei pyaingbwè - a Burmese regatta (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Image 2Sculpture of Myanmar mythical lion (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Image 3Political map of Burma (Myanmar) c. 1450 CE. (from History of Myanmar)
-
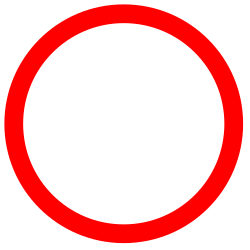
Image 5Military situation in Myanmar as of 2024[update]. Areas controlled by the Tatmadaw are highlighted in red. (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 8Boxing match, 19th-century watercolour (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Image 9Former US President Barack Obama poses barefoot on the grounds of Shwedagon Pagoda, one of Myanmar's major Buddhist pilgrimage sites. (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Image 11The restored Taungoo or Nyaungyan dynasty, c. 1650 CE (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 12A wedding procession, with the groom and bride dressed in traditional Burmese wedding clothes, reminiscent of royal attire (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Image 13Aung San Suu Kyi addresses crowds at the NLD headquarters shortly after her release. (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 14Recorder's Court on Sule Pagoda Road, with the Sule Pagoda at the far end, Rangoon, 1868. Photographer: J. Jackson. (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 15Saint Mary's Cathedral in Downtown Yangon is the largest Roman Catholic cathedral in Burma. (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Image 16Vegetable stall on the roadside at the Madras Lancer Lines, Mandalay, January 1886. Photographer: Hooper, Willoughby Wallace (1837–1912). (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 17British soldiers on patrol in the ruins of the Burmese town of Bahe during the advance on Mandalay, January 1945 (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 18A theatrical performance of the Mon dance (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Image 20The paddle steamer Ramapoora (right) of the British India Steam Navigation Company on the Rangoon river having just arrived from Moulmein. 1895. Photographers: Watts and Skeen. (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 21Myinhkin thabin - equestrian sport (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Image 2219th-century funeral cart and spire, which would form part of the procession from the home to the place of cremation (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Image 24A group of Buddhist worshipers at Shwedagon Pagoda, an important religious site for Burmese Buddhists (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Image 25The shores of Irrawaddy River at Nyaung-U, Bagan (from Geography of Myanmar)
-
Image 26Protesters in Yangon with a banner that reads "non-violence: national movement" in Burmese. In the background is Shwedagon Pagoda. (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 27Pagan Kingdom during Narapatisithu's reign. Burmese chronicles also claim Kengtung and Chiang Mai. Core areas shown in darker yellow. Peripheral areas in light yellow. Pagan incorporated key ports of Lower Burma into its core administration by the 13th century. (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 28Aerial view of a burned Rohingya village in Rakhine state, September 2017 (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 29A bull fight, 19th-century watercolour (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Image 30Two female musicians play the saung at a performance in Mandalay. (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Image 31British soldiers dismantling cannons belonging to King Thibaw's forces, Third Anglo-Burmese War, Ava, 27 November 1885. Photographer: Hooper, Willoughby Wallace (1837–1912). (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 32Salween river at Mae Sam Laep on the Thai-Myanmar border (from Geography of Myanmar)
-
Image 33British soldiers remove their shoes at the entrance of Shwedagon Pagoda. To the left, a sign reads "Foot wearing is strictly prohibited" in Burmese, English, Tamil, and Urdu. (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Image 34Grandfather Island, Dawei (from Geography of Myanmar)
-
Image 37Portuguese ruler and soldiers mounting an elephant. Jan Caspar Philips (draughtsman and engraver). (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 38Temples at Mrauk U, the capital of the Mrauk U Kingdom, which ruled over what is now Rakhine State (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 39A large fracture on the Mingun Pahtodawgyi caused by the 1839 Ava earthquake. (from Geography of Myanmar)
-
Image 40Protesters in Yangon carrying signs reading "Free Daw Aung San Suu Kyi" on 8 February 2021 (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 41Myanmar (Burma) map of Köppen climate classification (from Geography of Myanmar)
Major topics
Categories
More topics
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus












![Image 5Military situation in Myanmar as of 2024[update]. Areas controlled by the Tatmadaw are highlighted in red. (from History of Myanmar)](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/c1/Myanmar_civil_war.svg/120px-Myanmar_civil_war.svg.png)