User:Atlasxyz/sandbox
2024 Garut Earthquake
[edit]On 27 April 2024, at 23:29:47 WIB (UTC+7), a shallow Mw 6.2 earthquake struck in the Indian Ocean off the coast of West Java, Java Island, Indonesia. The epicenter was 156 km southwest of Garut Regency.
During the initial announcement of the earthquake, it was stated that the earthquake had a Mw of 6.5, at a depth of 10km.[1] This was later revised to Magnitude 6.2 and at a depth of 70km.[2]
| UTC time | 2024-04-27 16:29:47 |
|---|---|
| USGS-ANSS | ComCat |
| Local date | 27 April 2024 |
| Local time | 23:29:47 WIB |
| Duration | ~5-10 seconds |
| Magnitude | 6.2 Mw(BMKG) [3] |
| 6.1 Mw(USGS) [4] | |
| Depth | 70.0 km (43 mi) (BMKG)[3] |
| 59.7 km (37 mi) (USGS)[4] | |
| Epicenter | 8°00′18″S 107°16′48″E / 8.005°S 107.280°E |
| Fault | Unknown |
| Type | Thrust |
| Areas affected | Garut Regency, West Java, Jakarta |
| Total damage | Rp5,8 Billion |
| Max. intensity | MMI IV (Light) |
| Peak acceleration | 135 gal |
| Tsunami | No |
| Landslides | Yes |
| Aftershocks | Mw 3.1 [5] |
| Casualties | 4 injuries (BPBD) |
Tectonic setting
[edit]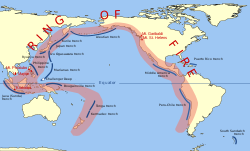

Indonesia lies in the Pacific Ring of Fire, and is the meeting point of 3 major tectonic plates, which are the Eurasian Plate, Indo-Australian Plate, and the Pacific Plate. This makes Indonesia one of the most prone countries to earthquake and volcanic eruption.
The Java Island lies near the Sunda Megathrust, an approximately 5,500 km (3,300 mi) long fault, which is an active convergent plate boundary where the Indo-Australian Plate is being subducted under the overriding Eurasian Plate.[6] This subduction zone is the main culprit to many giant, devastating earthquakes, including the 2004 Indian Ocean Earthquake and Tsunami.
Some parts of the megathrust, in particular, the Sunda Strait segment and the Mentawai-Suberut segment, has a particularly long seismic gap and contains a potential, respectively, Magnitude 8.7 and Magnitude 8.9 earthquake,[7] which the corresponding earthquake can produce tsunami with heights of up to 34 metres.[8]
Out of the four administrative provinces in Java, West Java is the most active in terms of seismic activity due to many sources of earthquake, which are: Subduction zone, undersea fault line, megathrust zone, and intraslab zone in the ocean, as well as fault lines on land, which some of them are: Lembang fault, Cimandiri fault, Baribis fault, and the Cugenang fault; a previously unknown fault that is responsible for the 2022 Cianjur Earthquake.[9]
Earthquake
[edit]The Mw 6.2 earthquake struck at 23:29:47 WIB, 27th April 2024, with it's epicenter being 156 km southwest of Garut Regency, at a depth of 70.0km. No tsunami warnings were issued.
The earthquake can be felt all across Garut Regency, West Java, Jakarta and as far as Yogyakarta.
Many people had thought at the time, that the earthquake was a Megathrust earthquake, this was later denied by BMKG stating that it was an intraslab earthquake that was caused by a deformation of rocks in the Indo-Australian Plate.
Intensity
[edit]Due to the earthquake striking at night (23:29:47 WIB), people across Garut Regency, West Java, as well as Jakarta were awoken from their sleep.
The BMKG had assigned the maximum intensity of the earthquake to be MMI IV (4). These intensities were recorded at Sukabumi and Tasikmalaya.
People across West Java and Sukabumi flocked to the streets as the ground shook. In Jakarta, people in hotels, apartments, and high rise buildings were evacuated.
- ^ Ghani, Hakim (28 April 2024). "Gempa M 6,5 di Garut, Warga: Lagi Tidur Tiba-tiba Bergetar" (in Indonesian). Detik.
- ^ Helmi, Isnaya (28 April 2024). "Gempa M 6,5 Guncang Garut, BMKG Ungkap Penyebabnya" (in Indonesian). Kompas.tv.
- ^ a b "Ulasan Guncangan Tanah Akibat Gempabumi Garut 27 April 2024 M6.2". Seismologi Teknik. BMKG.
- ^ a b "M 6.1 - 91 km S of Banjar, Indonesia". USGS.
- ^ "Gempa Garut 6.2, BMKG: Waspada Potensi Longsor dan Banjir Bandang Mengintai". 28 April 2024.
- ^ "Sunda megathrust", Wikipedia, 2023-05-27, retrieved 2024-09-13
- ^ Dwi, Chandra (4 September 2024). "Peringatan Keras! Ini 13 Wilayah yang Berpotensi Gempa Megathrust" (in Indonesian). CNBC Indonesia.
- ^ Redaksi (16 August 2024). "Bahaya Megathrust di Indonesia, Bisa Picu Tsunami 34 Meter" (in Indonesian). CNBC Indonesia.
- ^ Aida, Nur Rohmi; Hardiyanto, Sari (4 December 2022). "Mengapa Belakangan Jawa Barat Sering Diguncang Gempa? Ini Penjelasannya" (in Indonesian). Kompas.com.

