Portal:Maryland
|
Maryland Portal
|
Baltimore Task Force
|
Frederick Task Force
|
Montgomery Task Force
|
WikiProject Maryland
|
|
Main page
|
Discussion
|
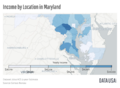
Introduction Maryland (US: /ˈmɛrɪlənd/ ⓘ MERR-il-ənd) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It borders the states of Virginia to its south, West Virginia to its west, Pennsylvania to its north, and Delaware to its east, as well as with the Atlantic Ocean to its east, and the national capital and federal district of Washington, D.C. to the southwest. With a total area of 12,407 square miles (32,130 km2), Maryland is the ninth-smallest state by land area, and its population of 6,177,224 ranks it the 18th-most populous state and the fifth-most densely populated. Maryland's capital city is Annapolis, and the state's most populous city is Baltimore. Maryland's coastline was first explored by Europeans in the 16th century. Prior to that, it was inhabited by several Native American tribes, mostly the Algonquian peoples. One of the original Thirteen Colonies, the Province of Maryland was founded in 1634 by George Calvert, 1st Baron Baltimore, a Catholic convert who sought to provide a religious haven for Catholics persecuted in England. In 1632, Charles I of England granted Lord Baltimore a colonial charter, naming the colony after his wife, Henrietta Maria. In 1649, the Maryland General Assembly passed an Act Concerning Religion, which enshrined the principle of toleration. Religious strife was common in Maryland's early years, and Catholics remained a minority, albeit in greater numbers than in any other English colony. Maryland's early settlements and population centers clustered around waterways that empty into the Chesapeake Bay. Its economy was heavily plantation-based and centered mostly on the cultivation of tobacco. Demand for cheap labor from Maryland colonists led to the importation of numerous indentured servants and enslaved Africans. In 1760, Maryland's current boundaries took form following the settlement of a long-running border dispute with Pennsylvania. Many of its citizens played key political and military roles in the American Revolutionary War. Although it was a slave state, Maryland remained in the Union during the American Civil War, and its proximity to Washington D.C. and Virginia made it a significant strategic location. After the Civil War ended in 1865, Maryland took part in the Industrial Revolution, driven by its seaports, railroad networks, and mass immigration from Europe. Since the 1940s, the state's population has grown rapidly, to approximately six million residents, and it is among the most densely populated U.S. states. As of 2015[update], Maryland had the highest median household income of any state, owing in large part to its proximity to Washington, D.C., and a highly diversified economy spanning manufacturing, retail services, public administration, real estate, higher education, information technology, defense contracting, health care, and biotechnology. Maryland is one of the most multicultural states in the country; it is one of the seven states where non-Whites compose a majority of the population, with the fifth-highest percentage of African Americans, and high numbers of residents born in Africa, Asia, Central America, and the Caribbean. The state's central role in U.S. history is reflected by its hosting of some of the highest numbers of historic landmarks per capita. (Full article...) This is a Featured article, which represents some of the best content on English Wikipedia..
 The Maryland House of Delegates is the lower house of the Maryland General Assembly, the state legislature of the U.S. State of Maryland. Three delegates are elected from each district, though some districts are divided into sub-districts. In the original state constitution, four delegates were elected from each county to one-year terms, and two were elected from each of the major early cities of Baltimore and Annapolis. Reforms in the 1830s, however, led to the apportionment of delegates by population rather than geography, and by 1922, delegates served four year terms. The modern system of apportionment of seats began in 1972, when 47 districts of roughly equal population were identified, although sub-districts were created to ensure local representation for areas with too little population to warrant an entire district. Delegates are elected in even years when the President of the United States is not being elected, similar to most other state offices in Maryland. The most recent election was in November 2022. Delegates are not term-limited. (Full article...) General imagesIn the news
On this day...The Maryland portal currently doesn't have any anniversaries listed for June 29. You can help by viewing the page source of an existing entry at /On this day to see how the entries should be formatted, then adding the missing entry. This is a Good article, an article that meets a core set of high editorial standards.
 The Crab Bowl Classic is the name given to the Maryland–Navy football rivalry. It is an American college football rivalry between the Maryland Terrapins football team of the University of Maryland and the Navy Midshipmen football team of the United States Naval Academy. The two institutions, located in close proximity in the state of Maryland, first met for a football game in 1905. Since then, the series has often been marked by controversy, with incidents by players and supporters occurring both on and off the field. The winner of the game is awarded the Crab Bowl trophy. Navy dominated the series early by winning the first eight games, between 1905 and 1930, which remains the longest streak. Maryland secured its first win in 1931 at a neutral site in Washington, D.C. After two more meetings, the series was suspended in 1934 when the Maryland administration protested a play. (Full article...) Selected article -The Baltimore and Ohio Railroad (reporting marks BO, B&O) was the oldest railroad in the United States and the first steam-operated common carrier. Construction of the line began in 1828, and it operated as B&O from 1830 until 1987, when it was merged into the Chessie System. Its lines are today controlled by CSX Transportation. Founded to serve merchants from Baltimore who wanted to do business with settlers crossing the Appalachian Mountains, the railroad competed with several existing and proposed turnpikes and canals, including the Erie and Chesapeake and Ohio Canal. The railroad began operation in 1830 on a 13-mile line between Baltimore and Ellicott's Mill in Maryland. Horse-drawn cars were replaced by steam locomotives the following year. (Full article...) Did you know?

SubcategoriesSelect [+] to view subcategories
TopicsRelated portalsAssociated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Discover Wikipedia using portals |