Portal:Anatomy
Introduction
Anatomy (from Ancient Greek ἀνατομή (anatomḗ) 'dissection') is the branch of morphology concerned with the study of the internal structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its beginnings in prehistoric times. Anatomy is inherently tied to developmental biology, embryology, comparative anatomy, evolutionary biology, and phylogeny, as these are the processes by which anatomy is generated, both over immediate and long-term timescales. Anatomy and physiology, which study the structure and function of organisms and their parts respectively, make a natural pair of related disciplines, and are often studied together. Human anatomy is one of the essential basic sciences that are applied in medicine, and is often studied alongside physiology.
Anatomy is a complex and dynamic field that is constantly evolving as discoveries are made. In recent years, there has been a significant increase in the use of advanced imaging techniques, such as MRI and CT scans, which allow for more detailed and accurate visualizations of the body's structures.
The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic parts. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal's body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of superficial anatomy. Microscopic anatomy involves the use of optical instruments in the study of the tissues of various structures, known as histology, and also in the study of cells. (Full article...)
Selected general anatomy article
Anatomical terminology is a specialized system of terms used by anatomists, zoologists, and health professionals, such as doctors, surgeons, and pharmacists, to describe the structures and functions of the body.
This terminology incorporates a range of unique terms, prefixes, and suffixes derived primarily from Ancient Greek and Latin. While these terms can be challenging for those unfamiliar with them, they provide a level of precision that reduces ambiguity and minimizes the risk of errors. Because anatomical terminology is not commonly used in everyday language, its meanings are less likely to evolve or be misinterpreted.
For example, everyday language can lead to confusion in descriptions: the phrase "a scar above the wrist" could refer to a location several inches away from the hand, possibly on the forearm, or it could be at the base of the hand, either on the palm or dorsal (back) side. By using precise anatomical terms, such as "proximal," "distal," "palmar," or "dorsal," this ambiguity is eliminated, ensuring clear communication. (Full article...)
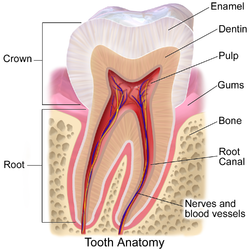
Selected anatomical feature
The gums or gingiva (pl.: gingivae) consist of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth. Gum health and disease can have an effect on general health. (Full article...)
Selected organ
The human skin is the outer covering of the body and is the largest organ of the integumentary system. The skin has up to seven layers of ectodermal tissue guarding muscles, bones, ligaments and internal organs. Human skin is similar to most of the other mammals' skin, and it is very similar to pig skin. Though nearly all human skin is covered with hair follicles, it can appear hairless. There are two general types of skin: hairy and glabrous skin (hairless). The adjective cutaneous literally means "of the skin" (from Latin cutis, skin).
Skin plays an important immunity role in protecting the body against pathogens and excessive water loss. Its other functions are insulation, temperature regulation, sensation, synthesis of vitamin D, and the protection of vitamin B folates. Severely damaged skin will try to heal by forming scar tissue. This is often discoloured and depigmented. (Full article...)
Selected biography
Abū al-Qāsim Khalaf ibn al-'Abbās al-Zahrāwī al-Ansari (Arabic: أبو القاسم خلف بن العباس الزهراوي; c. 936–1013), popularly known as al-Zahrawi (الزهراوي), Latinised as Albucasis or Abulcasis (from Arabic Abū al-Qāsim), was an Arab physician, surgeon and chemist from al-Andalus. He is considered one of the greatest surgeons of the Middle Ages.
Al-Zahrawi's principal work is the Kitab al-Tasrif, a thirty-volume encyclopedia of medical practices. The surgery chapter of this work was later translated into Latin, attaining popularity and becoming the standard textbook in Europe for the next five hundred years. Al-Zahrawi's pioneering contributions to the field of surgical procedures and instruments had an enormous impact in the East and West well into the modern period, where some of his discoveries are still applied in medicine to this day. He pioneered the use of catgut for internal stitches, and his surgical instruments are still used today to treat people. (Full article...)
Selected images
Categories
WikiProjects
Some Wikipedians have formed a project to better organize information in articles related to Anatomy. This page and its subpages contain their suggestions; it is hoped that this project will help to focus the efforts of other Wikipedians. If you would like to help, please swing by the talk page.
WikiProject Anatomy update
| new good articles since last newsletter include Thyroid, Hypoglossal nerve, Axillary arch, Human brain, Cerebrospinal fluid, Accessory nerve, Gallbladder, and Interventricular foramina (neuroanatomy) | |
| There is Introduction to Anatomy on Wikipedia published in the Journal of Anatomy [1] | |
| We reach two projects goals of 20 good articles, and less than half of our articles as stubs, in July 2017. Wikipedia talk:WikiProject Anatomy/Archive 11#Congratulations to all | |
| A discussion about two preferred section titles takes place here. |
Things to do
- Participate in discussions - a number of discussions such as those on our talk page or about our infobox would benefit from your opinion!
- Continue to add content to our articles
- Collaborate and discuss with other editors - many hands make light work!
- Help us simplify our anatomy articles
- Improve and update existing articles (lists of articles needing improvement)
- Example missing articles: Wikipedia:Requested articles/list of missing anatomy
- Reduce the number of stubs
Topics
Related portals
Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus