Portal:Tropical cyclones
The Tropical Cyclones Portal

A tropical cyclone is a storm system characterized by a large low-pressure center, a closed low-level circulation and a spiral arrangement of numerous thunderstorms that produce strong winds and heavy rainfall. Tropical cyclones feed on the heat released when moist air rises, resulting in condensation of water vapor contained in the moist air. They are fueled by a different heat mechanism than other cyclonic windstorms such as Nor'easters, European windstorms and polar lows, leading to their classification as "warm core" storm systems. Most tropical cyclones originate in the doldrums, approximately ten degrees from the Equator.
The term "tropical" refers to both the geographic origin of these systems, which form almost exclusively in tropical regions of the globe, as well as to their formation in maritime tropical air masses. The term "cyclone" refers to such storms' cyclonic nature, with anticlockwise rotation in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise rotation in the Southern Hemisphere. Depending on its location and intensity, a tropical cyclone may be referred to by names such as "hurricane", "typhoon", "tropical storm", "cyclonic storm", "tropical depression" or simply "cyclone".
Types of cyclone: 1. A "Typhoon" is a tropical cyclone located in the North-west Pacific Ocean which has the most cyclonic activity and storms occur year-round. 2. A "Hurricane" is also a tropical cyclone located at the North Atlantic Ocean or North-east Pacific Ocean which have an average storm activity and storms typically form between May 15 and November 30. 3. A "Cyclone" is a tropical cyclone that occurs in the South Pacific and Indian Oceans.
Selected named cyclone -
Typhoon Sarah, known as the Miyakojima Typhoon in Japan, was a destructive typhoon which was one of the strongest storms on record to strike South Korea and Russia. It formed during the peak of the busy 1959 Pacific typhoon season near Guam, and moved generally to the west-northwest. Continued observations from the hurricane hunters allowed the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) to track Sarah from its origins to its peak as a powerful typhoon, with maximum sustained winds estimated at 305 km/h (190 mph) on September 15. Shortly thereafter, the typhoon struck the small Japanese island of Miyako-jima, where the barometric pressure fell to 908.1 mbar (26.82 inHg), the second-lowest on record for the country. Sarah turned to the north and northeast, weakening from its peak intensity. On September 17, the typhoon made landfall just west of Busan, South Korea with winds of 185 km/h (115 mph), the nation's strongest landfall at the time and only to be surpassed by Typhoon Maemi in 2003. Sarah later became extratropical over the Japanese island of Hokkaido on September 18, although the remnants persisted for several days, crossing into the Russian Far East and later dissipating on September 23.
On Miyako-jima, Sarah damaged all of the crops and destroyed about 6,000 houses. Damage was estimated at $2 million, and there were seven deaths. The damage prompted the Japan Meteorological Agency to give Sarah the special name of the "Miyakojima Typhoon". However, the effects were worst in South Korea, and Sarah was described as the worst typhoon there in 50 years. Wind gusts there peaked at 169 km/h (105 mph), the highest at the time in the country. High winds and waves heavily damaged the port of Busan. Nationwide, the storm destroyed over 14,000 homes and left 782,126 people homeless, causing over $100 million in damage. At least 669 people were killed in South Korea, and an additional 1,200 fishermen were lost offshore the country. In Japan, widespread flooding killed 47 people and destroyed 16,632 homes. (Full article...)
Selected article -
The effects of Hurricane Georges in Cuba included $305.8 million in damages and six deaths. Forming out of a tropical wave over the Atlantic Ocean, Georges attained a peak intensity of 155 mph (249 km/h) on September 20, 1998. On September 23, the storm made landfall in southeastern Cuba as a minimal Category 1 hurricane. The storm tracked over the county for the following two days before emerging into the Gulf of Mexico on September 25 and later making landfall in the United States as a Category 2 hurricane. Before the storm's landfall in Cuba, officials reported that 200,000 people were evacuated to shelters; however, later reports indicated that upwards 711,000 people evacuated. A state of emergency was declared for much of eastern Cuba and most of the country was placed under a tropical storm or hurricane warning during the storm's passage.
More than 3,000 homes were destroyed and 60,000 damaged throughout the country, leaving an estimated 100,000 people homeless. Agricultural losses were severe, with the plantain crop loss estimated at 70% of annual production due to Georges, accounting for roughly $15 million of the total damages. Following the passage of the hurricane, several countries provided relief funds to Cuba for disaster recovery. Despite crop losses, affected residents were given essential supplies by the local government. By December, an estimated $90 million in funds was allocated for the impacts of Georges and the drought that preceded it. (Full article...)
Selected image -

Selected season -

The 2002 Pacific hurricane season was an average season which produced fifteen named storms. Eight hurricanes formed, including a record-equaling three Category 5 hurricanes, a record it shares with the 1994 and 2018 seasons. It was also a near-average season in terms of accumulated cyclone energy (ACE), having an ACE of 125. The season officially began on May 15, 2002 in the East Pacific Ocean, and on June 1, 2002 in the Central Pacific; both ended on November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclone formation occurs in these regions of the Pacific. The first system of the 2002 season, Hurricane Alma, formed on May 24, and the last, Tropical Depression Sixteen-E, dissipated on November 16.
The strongest hurricane of the season, Kenna, formed on October 22 and peaked as a Category 5 hurricane two days later. Land impact was relatively significant. Kenna made landfall near Puerto Vallarta, located in the Mexican state of Jalisco on October 25, killing four people. Kenna was, at the time, the second-most powerful hurricane to ever strike the western coast of Mexico, hitting with winds of 140 mph (220 km/h), as well as the strongest landfall in terms of windspeed until Hurricane Patricia in 2015. Elsewhere, Tropical Storm Julio made landfall in Mexico, and Tropical Storm Boris dumped torrential rain along the Mexican coast, despite remaining offshore. Hurricanes Elida and Hernan also reached Category 5 intensity, but neither caused any damage. Damage across the basin reached $101.23 million (2002 USD), while 7 people were killed by Julio and Kenna. (Full article...)
Related portals
Currently active tropical cyclones
Italicized basins are unofficial.
- North Atlantic (2025)
- No active systems
- North Indian Ocean (2025)
- No active systems
- Mediterranean (2025–26)
- No active systems
- South-West Indian Ocean (2025–26)
- No active systems
- Australian region (2025–26)
- No active systems
- South Pacific (2025–26)
- No active systems
- South Atlantic (2025–26)
- No active systems
Last updated: 20:41, 10 August 2025 (UTC)
Tropical cyclone anniversaries

- 2006 - Typhoon Saomai (pictured) made landfall on the coast of Zhejiang, China as a violent typhoon. Saomai killed over 400 people and caused $1.5 billion of damage.

August 11,
- 1856 - The 1856 Last Island hurricane made landfall in Louisiana as a Category 4 hurricane, obliterating Last Island (a.k.a. Isle Dernière). At least 200 people were killed.
- 1987 - Typhoon Betty (pictured) reaches peak intensity with 1-minute sustained winds of 260 km/h (160 mph) with a pressure of 890 hPa while making landfall over northern Samar.

- August 12, 2004 - Typhoon Rananim (pictured) reached its peak intensity to the east of Taiwan with 170 km/h (105 mph) winds. Ranamin later made landfall in Zhejiang, China killing 115 people and causing over $4 billion in damage.
Did you know…


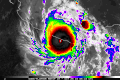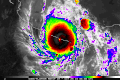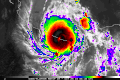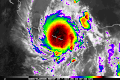
- …that the Joint Typhoon Warning Center considers that Typhoon Vera (pictured) of 1986 is actually two distinct systems, formed from two separated low-level circulations?
- …that Cyclone Freddy (track pictured) in 2023 was the longest-lasting tropical cyclone recorded?
- …that the typhoons of 2024—Yinxing, Toraji, Usagi, and Man-yi (pictured)—made history as the first recorded instance since 1951 of four tropical cyclones coexisting in November?
- …that Hurricane Otis (pictured) in 2023 was the first Pacific hurricane to make landfall at Category 5 intensity and surpassed Hurricane Patricia as the strongest landfalling Pacific hurricane on record?
General images -

A Category 5 Atlantic hurricane is a tropical cyclone that reaches Category 5 intensity on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale, within the Atlantic Ocean to the north of the equator. They are among the strongest tropical cyclones that can form on Earth, having 1-minute sustained wind speeds of at least 137 knots (254 km/h; 158 mph; 70 m/s). The United States National Hurricane Center currently estimates that 11 tropical cyclones between 1851 (the first Atlantic hurricane season to be included in the official Atlantic tropical cyclone record) and 1959 peaked as Category 5 hurricanes. However, because technologies such as satellite monitoring were not available until the 1960s, some cyclones may have remained undetected. Since 1960, 31 Atlantic hurricanes have reached Category 5. (Full article...)
Topics
Subcategories
Related WikiProjects
WikiProject Tropical cyclones is the central point of coordination for Wikipedia's coverage of tropical cyclones. Feel free to help!
WikiProject Weather is the main center point of coordination for Wikipedia's coverage of meteorology in general, and the parent project of WikiProject Tropical cyclones. Three other branches of WikiProject Weather in particular share significant overlaps with WikiProject Tropical cyclones:
- The Non-tropical storms task force coordinates most of Wikipedia's coverage on extratropical cyclones, which tropical cyclones often transition into near the end of their lifespan.
- The Floods task force takes on the scope of flooding events all over the world, with rainfall from tropical cyclones a significant factor in many of them.
- WikiProject Severe weather documents the effects of extreme weather such as tornadoes, which landfalling tropical cyclones can produce.
Things you can do
 |
Here are some tasks awaiting attention:
|
Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus







































