Leopardus
| Leopardus | |
|---|---|

| |
| Leopardus species from top-left, clockwise: ocelot (L. pardalis), oncilla (L. tigrinus), Pampas cat (L. colocola), kodkod (L. guigna), margay (L. wiedii), Geoffroy's cat (L. geoffroyi) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Suborder: | Feliformia |
| Family: | Felidae |
| Subfamily: | Felinae |
| Genus: | Leopardus Gray, 1842 |
| Type species | |
| Leopardus griseus[2] Gray, 1842
| |

| |
| Leopardus distribution | |
Leopardus is a genus comprising eight species of small cats native to the Americas.[3] This genus is considered the oldest branch of a genetic lineage of small cats in the Americas whose common ancestor crossed the Bering land bridge from Asia to North America in the late Miocene.[4]
Characteristics
[edit]Leopardus species have spotted fur, with ground colors ranging from pale buff, ochre, fulvous and tawny to light gray.[5] Their small ears are rounded and white-spotted; their rhinarium is prominent and naked above, and their nostrils are widely separated.[6] They have 36 chromosomes, whereas other felids have 38.[7]
Taxonomy
[edit]The generic name Leopardus was proposed by John Edward Gray in 1842, when he described two spotted cat skins from Central America and two from India in the collection of the Natural History Museum, London.[8] Several genera were proposed in the 19th and early 20th centuries for small spotted cats in the Americas, including:
- Dendrailurus, Lynchailurus, Noctifelis, Oncifelis and Oncoïdes by Nikolai Severtzov in 1858;[9]
- Margay, Pajeros, Pardalina and Pardalis by Gray in 1867;[10]
- Oncilla by Joel Asaph Allen in 1919;[11]
- Oreailurus by Ángel Cabrera in 1940;[12]
- Colocolo by Reginald Innes Pocock in 1941.[13]
Analysis of skull morphology of these taxa revealed close similarities in their base of skulls and nasal bones, their masticatory muscles, and dentition.[14] Phylogenetic analysis of tissue samples of these taxa and their ability to hybridise support the notion that they are members of the same genus.[4][7] The following eight extant Leopardus species have commonly been recognized as valid taxa since 2017:[3]
| Name | IUCN Red List status and distribution |
|---|---|
Ocelot L. pardalis (Linnaeus, 1758)[15]
|
LC[16]
|
Oncilla L. tigrinus (Schreber, 1775)[17]
|
VU[18]
|
Pampas cat L. colocola (Molina, 1782)[19]
|
NT[20]
Range includes multiple species |
Kodkod L. guigna (Molina, 1782)[19]
|
VU[21]
|
Margay L. wiedii (Schinz, 1821)[22]
|
NT[23]
|
Geoffroy's cat L. geoffroyi (d'Orbigny & Gervais, 1844)[24]
|
LC[25]
|
Andean mountain cat L. jacobita (Cornalia, 1865)[26]
|
EN[27]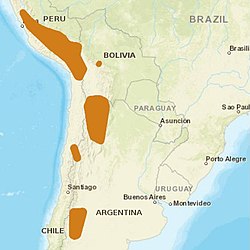
|
Southern tigrina L. guttulus (Hensel, 1872)[28]
|
VU[29]
|
Additionally, more recent genetic analyses in 2017 and 2021 proposed the recognition of a third tigrina-like species, Leopardus emiliae.[30][31]
A 2021 analysis of 142 pampas cat museum specimen collected across South America showed significant morphological differences between them. Therefore, it was proposed to split the historically-contentious pampas cat species complex into five species: Leopardus colocolo, Leopardus braccatus, Leopardus garleppi, Leopardus munoai, and Leopardus pajeros.[32] Later that same year, it was noted that the oldest available name for pampas cats of the Uruguayan savannah region was Leopardus fasciatus, not L. munoai.[33]
Another study in 2023 described another new species, Leopardus narinensis, based on a single dried skin collected in 1989 on the Galeras Volcano in the Nariño Department of Colombia. They found it to be very different from all other Leopardus species both morphologically and genetically.[34]
A different study in 2024 did a detailed analysis of both the morphology and genetics of specimens assigned to Leopardus tigrinus, Leopardus guttulus, and Leopardus emiliae. It suggested L. t. pardinoides should be elevated to species status as Leopardus pardinoides due to significant differences in morphology, genetics, and ecology. The study also assigned the subspecies L. t. oncilla to be a subspecies of L. pardinoides as L. p. oncilla. Additionally, genetic analysis suggested that Leopardus emiliae was not genetically distinct from L. tigrinus, and thus may be invalid. The study recommended the common names savannah tiger-cat for L. tigrinus, Atlantic Forest tiger-cat for L. guttulus, and clouded tiger-cat for L. pardinoides.[35]
An expanded list of Leopardus species would be:[36]
- Leopardus braccatus, the Pantanal cat or Brazilian pampas cat
- Leopardus colocola, the colocolo or Central Chilean pampas cat
- Leopardus emiliae, the eastern tigrina or Snethlage's tigrina
- Leopardus fasciatus, Muñoa’s pampas cat or Uruguayan pampas cat
- Leopardus garleppi, the northern pampas cat or Garlepp's pampas cat
- Leopardus geoffroyi, Geoffroy's cat
- Leopardus guigna, the kodkod
- Leopardus guttulus, the southern tigrina or Atlantic Forest tiger-cat
- Leopardus jacobita, the Andean mountain cat
- Leopardus narinensis, the Nariño cat, Galeras cat, or red tigrina[34]
- Leopardus pajeros, the southern pampas cat
- Leopardus pardalis, the ocelot
- Leopardus pardinoides, the clouded tiger-cat
- Leopardus tigrinus, the oncilla, northern tigrina, or savannah tiger-cat
- Leopardus weidii, the margay
Phylogeny
[edit]Phylogenetic analysis of the nuclear DNA in tissue samples from all Felidae species revealed that the evolutionary radiation of the Felidae began in Asia in the Miocene around 14.45 to 8.38 million years ago.[4] Analysis of mitochondrial DNA of all Felidae species indicates a radiation at around 16.76 to 6.46 million years ago.[37]
The last common ancestor of Leopardus, Puma and Lynx is estimated to have lived 10.95 to 6.3 million years ago, based on analysis of nuclear DNA of cat species.[4] Analysis of their mitochondrial DNA indicates that their last common ancestor lived 14.04 to 6.83 million years ago.[37] Leopardus forms an evolutionary lineage that genetically diverged between 4.25 to 2.02 million years ago[4] and 5.19 to 0.98 million years ago.[37] It crossed the Isthmus of Panama probably during the Great American Biotic Interchange in the late Pliocene.[4] Leopardus vorohuensis is an extinct species of the genus, of which fossils were found in the Argentinian Vorohué Formation dated to the early Pleistocene; its supraorbital foramen and shape of teeth resemble those of the pampas cat.[1]
Within the genus, three distinct clades were identified: one comprising the ocelot and the margay, a second the Andean mountain cat and Pampas cat, and the third the kodkod, oncilla and Geoffroy's cat.[38][39] The following cladogram shows estimated divergence times in million years ago (mya).
| nuclear DNA:[4] |
|---|
| mitochondrial DNA:[37] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
References
[edit]- ^ a b Berta, A. (1983). "A new species of small cat (Felidae) from the late Pliocene – early Pleistocene (Uquian) of Argentina". Journal of Mammalogy. 64 (4): 720–725. doi:10.2307/1380541. JSTOR 1380541.
- ^ Wozencraft, W. C. (2005). "Genus Leopardus". In Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 537–540. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- ^ a b Kitchener, A. C.; Breitenmoser-Würsten, C.; Eizirik, E.; Gentry, A.; Werdelin, L.; Wilting, A.; Yamaguchi, N.; Abramov, A. V.; Christiansen, P.; Driscoll, C.; Duckworth, J. W.; Johnson, W.; Luo, S.-J.; Meijaard, E.; O’Donoghue, P.; Sanderson, J.; Seymour, K.; Bruford, M.; Groves, C.; Hoffmann, M.; Nowell, K.; Timmons, Z.; Tobe, S. (2017). "A revised taxonomy of the Felidae: The final report of the Cat Classification Task Force of the IUCN Cat Specialist Group" (PDF). Cat News (Special Issue 11): 46–58.
- ^ a b c d e f g Johnson, W. E.; Eizerik, E.; Pecon-Slattery, J.; Murphy, W. J.; Antunes, A.; Teeling, E. & O'Brien, S. J. (2006). "The Late Miocene radiation of modern Felidae: A genetic assessment". Science. 311 (5757): 73–77. Bibcode:2006Sci...311...73J. doi:10.1126/science.1122277. PMID 16400146. S2CID 41672825.
- ^ Allen J. A. (1919). "Notes on the synonymy and nomenclature of the smaller spotted cats of tropical America". Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History. 41: 341–419.
- ^ Pocock, R. I. (1917). "The classification of the existing Felidae". Annals and Magazine of Natural History. Series 8. XX (119): 329–350. doi:10.1080/00222931709487018.
- ^ a b Trigo T. C.; Freitas T. R. O.; Kunzler G.; Cardoso L.; Silva J. C. R.; Johnson, W. E.; O’Brien S. J.; Bonatto S. L. & Eizirik E. (2008). "Inter-species hybridization among Neotropical cats of the genus Leopardus, and evidence for an introgressive hybrid zone between L. geoffroyi and L. tigrinus in southern Brazil". Molecular Ecology. 17 (19): 4317–4333. Bibcode:2008MolEc..17.4317T. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2008.03919.x. PMC 6993176. PMID 18785898.
- ^ Gray, J. E. (1842). "Descriptions of some new genera and fifty unrecorded species of Mammalia". Annals and Magazine of Natural History. 10 (65): 255–267. doi:10.1080/03745484209445232.
- ^ Severtzow, M. N. (1858). "Notice sur la classification multisériale des Carnivores, spécialement des Félidés, et les études de zoologie générale qui s'y rattachent". Revue et Magasin de Zoologie Pure et Appliquée. X: 385–396.
- ^ Gray, J. E. (1867). "Notes on the skulls of the Cats (Felidae)". Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London (March): 258–277.
- ^ Allen, J. A. (1919). "Severtzow's classification of the Felidae" (PDF). Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History. 41 (6): 335–342.
- ^ Cabrera, Á. (1940). "Notas sobre Carnívoros sudamericanos" (PDF). Notas del Museo de la Plata. V (29): 1–22.
- ^ Pocock, R.I. (1941). "The Examples of the Colocolo and of the Pampas Cat in the British Museum". The Annals and Magazine of Natural History. 7 (39): 257–274. doi:10.1080/03745481.1941.9727931.
- ^ Salles, L. O. (1992). Felid phylogenetics: extant taxa and skull morphology (Felidae, Aeluroidea) (PDF). American Museum Novitates. Vol. 3047. New York: American Museum of Natural History.
- ^ Linnaeus, C. (1758). "Felis pardalis". Systema naturae per regna tria naturae: secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis. Vol. I (Tenth ed.). Holmiae: Laurentius Salvius. p. 42.
- ^ Paviolo, A.; Crawshaw, P.; Caso, A.; de Oliveira, T.; Lopez-Gonzalez, C.A.; Kelly, M.; De Angelo, C. & Payan, E. (2016) [errata version of 2015 assessment]. "Leopardus pardalis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T11509A97212355.
- ^ Schreber, J. C. D. (1778). "Die Maragua". Die Säugethiere in Abbildungen nach der Natur, mit Beschreibungen. Erlangen: Wolfgang Walther. pp. 396–397.
- ^ Payan, E. & de Oliveira, T. (2016). "Leopardus tigrinus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T54012637A50653881.
- ^ a b Molina, G. I. (1782). "La Guigna Felis guigna". Saggio sulla storia naturale del Chilli. Bologna: Stamperia di S. Tommaso d’Aquino. p. 295. Archived from the original on 2019-06-08. Retrieved 2019-03-25.
- ^ Lucherini, M.; Eizirik, E.; de Oliveira, T.; Pereira, J.; Williams, R.S.R. (2016). "Leopardus colocolo". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T15309A97204446.
- ^ Napolitano, C.; Gálvez, N.; Bennett, M.; Acosta-Jamett, G. & Sanderson, J. (2015). "Leopardus guigna". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T15311A50657245. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
- ^ Schinz, H. R. (1821). "Wiedische Katze Felis wiedii". Das Thierreich eingetheilt nach dem Bau der Thiere: als Grundlage ihrer Naturgeschichte und der vergleichenden Anatomie von dem Herrn Ritter von Cuvier. Säugethiere und Vögel, Volume 1. Stuttgart, Tübingen: Cotta. pp. 235–236.
- ^ de Oliveira, T.; Paviolo, A.; Schipper, J.; Bianchi, R.; Payan, E. & Carvajal, S.V. (2015). "Leopardus wiedii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T11511A50654216.
- ^ D'Orbigny, A. & Gervais, P. (1844). "Mammalogie: Nouvelle espèce de Felis". Extraits des Procès-verbaux des Séances. 9: 40–41.
- ^ Pereira, J.; Lucherini, M. & Trigo, T. (2015). "Leopardus geoffroyi". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T15310A50657011.
- ^ Cornalia, E. (1865). "Descrizione di una nuova specie del genere Felis. Felis jacobita (Corn.)". Memorie della Societá Italiana di Scienze Naturali. 1: 3–9.
- ^ Villalba, L.; Lucherini, M.; Walker, S.; Lagos, N.; Cossios, D.; Bennett, M. & Huaranca, J. (2016). "Leopardus jacobita". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T15452A50657407.
- ^ Hensel, R. (1872). "Beiträge zur Kenntniss der Säugethiere Süd-Brasiliens". Physikalische Abhandlungen der Königlichen Akademie der Wissenschaften zu Berlin (1873): 1–130.
- ^ de Oliveira, T.; Trigo, T.; Tortato, M.; Paviolo, A.; Bianchi, R. & Leite-Pitman, M. R. P. (2016). "Leopardus guttulus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T54010476A54010576.
- ^ do Nascimento, F.O.; Feijó, A. (2017). "Taxonomic revision of the tigrina Leopardus tigrinus (Schreber, 1775) species group (Carnivora, Felidae)". Papéis Avulsos de Zoologia. 57 (19): 231–264. doi:10.11606/0031-1049.2017.57.19.
- ^ Trindade, Fernanda J.; Rodrigues, Maíra R.; Figueiró, Henrique V.; Li, Gang; Murphy, William J.; Eizirik, Eduardo (2021). "Genome-Wide SNPS Clarify a Complex Radiation and Support Recognition of an Additional Cat Species". Molecular Biology and Evolution. 38 (11): 4987–4991. doi:10.1093/molbev/msab222. PMC 8557425. PMID 34320647.
- ^ Nascimento, F.O.D.; Cheng, J. & Feijó, A. (2021). "Taxonomic revision of the pampas cat Leopardus colocola complex (Carnivora: Felidae): an integrative approach". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 191 (2): 575–611. doi:10.1093/zoolinnean/zlaa043.
- ^ Martínez-Lanfranco, Juan Andrés; González, Enrique M. (2022). "The oldest available name for the pampas cat of the Uruguayan Savannah ecoregion is Leopardus fasciatus (Larrañaga 1923)". Therya. 13 (3): 259–264. doi:10.12933/therya-22-1187. S2CID 252649692.
- ^ a b Manuel Ruiz-Garcia; Myreya Pinedo-Castro; Joseph Mark Shostell (2023). "Morphological and Genetics Support for a Hitherto Undescribed Spotted Cat Species (Genus Leopardus; Felidae, Carnivora) from the Southern Colombian Andes". Genes. 14 (6): 1266. doi:10.3390/GENES14061266. ISSN 2073-4425. PMC 10298493. PMID 37372446. Wikidata Q121764991.
- ^ de Oliveira, Tadeu G.; Fox-Rosales, Lester A.; Ramírez-Fernández, José D. (2024). "Ecological modeling, biogeography, and phenotypic analyses setting the tiger cats' hyperdimensional niches reveal a new species". Scientific Reports. 14 (1): 2395. Bibcode:2024NatSR..14.2395D. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-52379-8. PMC 10825201. PMID 38287072.
- ^ *"Leopardus". ASM Mammal Diversity Database. American Society of Mammalogists. Retrieved 8 December 2023.
- ^ a b c d Li, G.; Davis, B. W.; Eizirik, E. & Murphy, W. J. (2016). "Phylogenomic evidence for ancient hybridization in the genomes of living cats (Felidae)". Genome Research. 26 (1): 1–11. doi:10.1101/gr.186668.114. PMC 4691742. PMID 26518481.
- ^ Johnson, W.E.; Dratch, P.A.; Martenson, J.S. & O'Brien, S.J. (1996). "Resolution of recent radiations within three evolutionary lineages of Felidae using mitochondrial restriction fragment length polymorphism variation". Journal of Mammalian Evolution. 3 (2): 297–120. doi:10.1007/BF01454358. S2CID 38348868.
- ^ Johnson, W. E.; Culver, M.; Iriarte, J. A.; Eizirik, E.; Seymour, K. L. & O'Brien, S. J. (1998). "Tracking the evolution of the elusive Andean mountain cat (Oreailurus jacobitus) from mitochondrial DNA" (PDF). Journal of Heredity. 89 (3): 227–232. doi:10.1093/jhered/89.3.227. PMID 9656464.
External links
[edit]- "Leopardus". ASM Mammal Diversity Database. 1.5. American Society of Mammalogists. Retrieved 26 August 2021.
