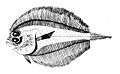
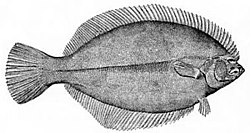
Bothidae
Appearance
(Redirected from Lefteye flounder)
| Lefteye flounders Temporal range:
| |
|---|---|

| |
| Scaldfish, Arnoglossus laterna | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Actinopterygii |
| Order: | Carangiformes |
| Suborder: | Pleuronectoidei |
| Family: | Bothidae Smitt, 1892 |
| Type genus | |
| Bothus Rafinesque, 1810
| |
| Genera | |
|
See text | |
Bothidae or lefteye flounders are a family of flounders. They are called "lefteye flounders" because most species lie on the sea bottom on their right sides, with both eyes on their left sides.[1] The family is also distinguished by the presence of spines on the snout and near the eyes.[2]
Lefteye flounders vary considerably in size between the more than 160 species, ranging from 4.5 cm (1.8 in) to 1.5 m (4.9 ft) in length.[2]
Taxonomy
[edit]The following genera are placed in this family:
- Arnoglossus
- Asterorhombus
- Bothus
- Chascanopsetta
- Crossorhombus
- Engyophrys
- Engyprosopon
- Grammatobothus
- Japonolaeops
- Kamoharaia
- Laeops
- Lophonectes
- Monolene
- Neolaeops
- Parabothus
- Perissias
- Psettina
- Taeniopsetta
- Tosarhombus
- Trichopsetta
The following fossil genera are also known:
- †Miobothus Chanet & Schultz, 1994 (Middle Miocene of Austria)[3]
- †Oligobothus Baciu & Chanet, 2002 (Early Oligocene of Romania and Poland)[4][5]
- †Oranobothus Chanet, 1996 (latest Miocene of Algeria)[6]
Gallery
[edit]-
Scaldfish (Arnoglossus laterna) larva
-
Wide-eyed flounder, Bothus podas
-
Deepwater flounder, Monolene sessilicauda
-
Sash flounder, Trichopsetta ventralis
See also
[edit]- Pleuronectidae, the righteye family of flounders
References
[edit]- ^ Froese, Rainer; Pauly, Daniel (eds.). "Family Bothidae". FishBase. February 2006 version.
- ^ a b Chapleau, Francois & Amaoka, Kunio (1998). Paxton, J.R. & Eschmeyer, W.N. (eds.). Encyclopedia of Fishes. San Diego: Academic Press. pp. 224–225. ISBN 0-12-547665-5.
- ^ Chanet, Bruno; Schultz, Orwin (1994). "Pleuronectiform fishes from the Upper Badenian (Middle Miocene) of St. Margarethen (Austria)" (PDF). Ann. Naturhist. Mus. Wien (96): 95–115.
- ^ Campbell, Matthew A.; Chanet, Bruno; Chen, Jhen-Nien; Lee, Mao-Ying; Chen, Wei-Jen (2019). "Origins and relationships of the Pleuronectoidei: Molecular and morphological analysis of living and fossil taxa". Zoologica Scripta. 48 (5): 640–656. doi:10.1111/zsc.12372. ISSN 1463-6409.
- ^ Kovalchuk, Oleksandr; Bienkowska-Wasiluk, Małgorzata; Dubikovska, Anastasiia; Świdnicka, Ewa; Stefaniak, Krzysztof; Khekalo, Olga; Barkaszi, Zoltán. "Oligocene flatfishes (Teleostei, Pleuronectiformes) of the Outer Carpathian Basin". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 0 (0): e2520490. doi:10.1080/02724634.2025.2520490. ISSN 0272-4634.
- ^ "Oranobothus arambourgi n.g. n.sp.(Pisces, Pleuronectiformes, Bothidae) provenant du Messinien (Miocène supérieur) d'Oran (Algérie)". Bulletin du Muséum national d'Histoire naturelle, 4ème série – section C – Sciences de la Terre, Paléontologie, Géologie, Minéralogie. 18 (4): 555–568. 1996.